What is EDI?
EDI services to meet the needs of every business.
What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange simplified.
Business documents can be shared easily. The most common ones are Purchase Orders, Invoices, Ship Notices, Status Updates, but there are many other specific documents that pertain to various industries.
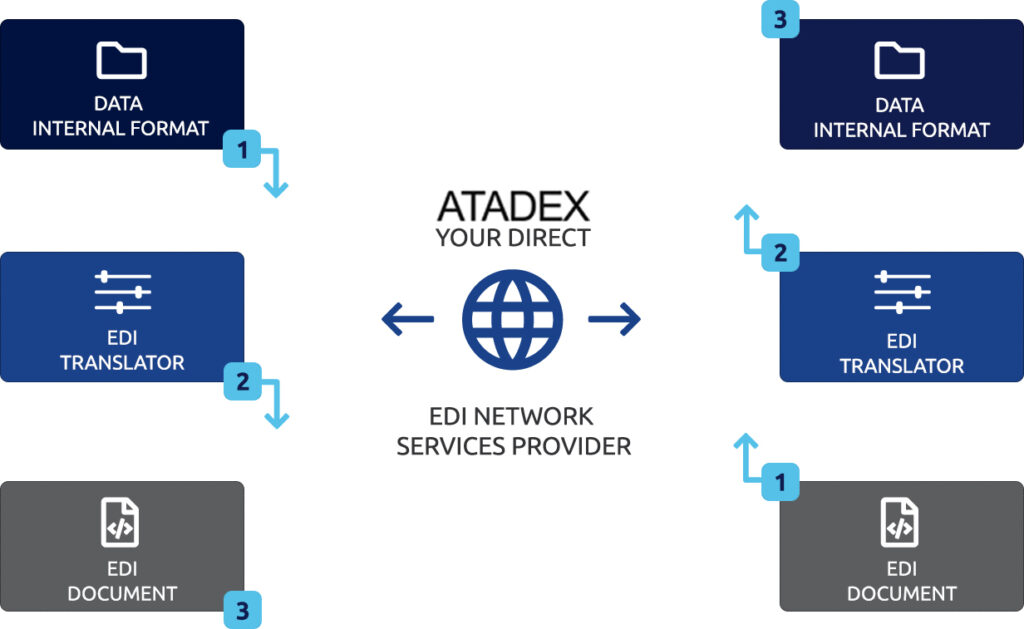
Most common EDI standards are ANSI X12 and EDIFACT. For each standard, there are many versions (e.g., X12 4010, X12 5010, D97A, etc.). Businesses typically use an EDI translator – either as in-house software or via an EDI service provider – to translate the EDI format so the data can be used by their internal applications and enable full integration of such business documents.
The benefits of a properly implemented, fully integrated EDI system can be seen throughout the operations of the business in several ways:
Reduced manual intervention.
Information is integrated systematically eliminating delays and transposition errors that come from manual input.
Improved data accuracy.
The information is accurate and timely as it comes directly from the customer/supplier system.
Enhanced operational efficiency.
With actionable information at their fingertips, your customer facing associates can get more done in less time.
Quicker invoicing.
Leads to prompter settlement – As more of a company’s applications are integrated into EDI, its cash flow will improve due to overall efficiencies that EDI provides.
Superior customer satisfaction.
Elimination of errors, better customer service, and customers kept in the know with real time information, allow them to plan their business more effectively.
Reduced costs.
Correcting errors costs an organization both time and money; so, the reduction of errors also reduces costs.
Greater profitability.
Each of the areas highlighted above make for a more profitable business. EDI integration not only makes a business more profitable on their existing customer base but sets a strong foundation for growth.
What is API/WEB services?
The Modern API
Over the years, what an “API” is has often described any sort of generic connectivity interface to an application. More recently, however, the modern API has taken on some characteristics that make them extraordinarily valuable and useful:
- Modern APIs adhere to standards (typically HTTP and REST), that are developer-friendly, easily accessible and understood broadly
- They are treated more like products than code. They are designed for consumption for specific audiences (e.g., mobile developers), they are documented, and they are versioned in a way that users can have certain expectations of its maintenance and lifecycle.
- Because they are much more standardized, they have a much stronger discipline for security and governance, as well as monitored and managed for performance and scale
- As any other piece of productized software, the modern API has its own software development lifecycle (SDLC) of designing, testing, building, managing, and versioning. Also, modern APIs are well documented for consumption and versioning.
Web Services
a complete web service is any service that −
- Is available over the Internet or private (intranet) networks
- Uses a standardized XML messaging system
- Is not tied to any one operating system or programming language
- Is self-describing via a common XML grammar
- Is discoverable via a simple find mechanism

